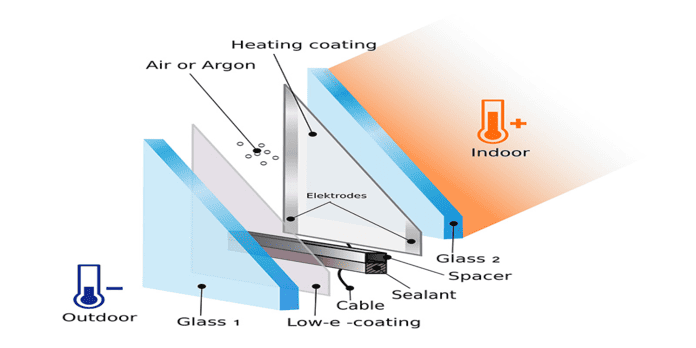
Electric Heated Glass
Electrically heated glass, also known as heated glass or electrically conductive glass, is a type of glass that incorporates a transparent conductive coating and an electrical circuit to generate heat. This technology is used to prevent condensation, ice, and snow buildup on glass surfaces, making it particularly useful in various applications, including automotive, architectural, and even in some specialized industrial settings.
Its power consumption is depending on the glass applications and the available glazing surface, the power of the heated glazing to be used (averaged data) is, according to the manufacturers:
from 50 to 100 W/m2 for an anti-condensation application,
from 100 to 250 W/m2 for auxiliary heating,
from 250 to 500 W/m2 for main heating
from 350 to 700 W/m2 for a snow removal function (glazed roof).
Applications
- Automotive
Windshields: Prevents ice and snow buildup, improving visibility and safety.
Rear Windows: Commonly used as defrosters to clear condensation and frost.
Side Mirrors: Prevents fogging and icing, enhancing rear visibility. - Architectural
Windows and Facades: Prevents condensation on large glass surfaces in buildings, maintaining clear views and reducing maintenance.
Skylights: Keeps skylights clear of snow and ice, ensuring natural light entry.
Greenhouses: Maintains optimal temperatures and prevents frost on glass surfaces. - Specialized Industrial
Refrigerated Display Cases: Prevents condensation on glass doors in commercial refrigeration units.
Laboratories and Clean Rooms: Maintains clear vision panels by preventing condensation in controlled environments