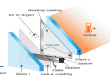
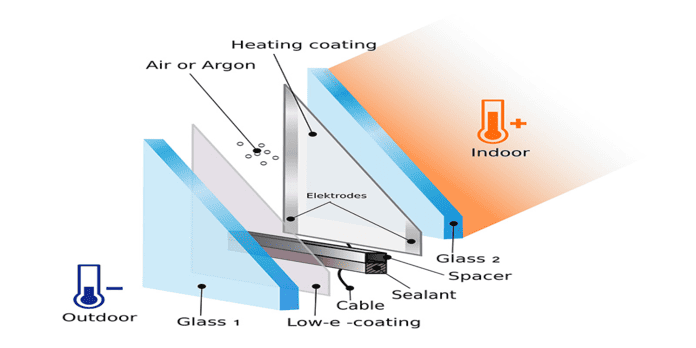
Electrically heated glass, also known as heated glass or electrically conductive glass, is a type of glass that incorporates a thin, transparent conductive coating or embedded wires that can generate heat when an electrical current is applied. This technology is used to prevent the buildup of condensation, ice, and frost on glass surfaces, ensuring clear visibility and maintaining comfort.
How Electrically Heated Glass Works
Electrically heated glass typically uses one of the following methods to generate heat:
Conductive Coating:
A thin layer of a transparent conductive oxide (such as indium tin oxide, ITO) is applied to the glass surface.
When an electrical current passes through this coating, it generates heat, which is evenly distributed across the glass surface.
Embedded Wires:
Fine, electrically conductive wires (often made of tungsten or nichrome) are embedded within the glass or laminated between two layers of glass.These wires heat up when an electrical current flows through them, providing localized heating to the glass surface.
Key Features
1.Anti-Condensation and Anti-Frost:
Prevents the buildup of condensation, frost, and ice on glass surfaces, ensuring clear visibility.
Ideal for environments with high humidity or cold temperatures.
2.Uniform Heating:
Provides consistent and even heating across the entire glass surface, minimizing cold spots and ensuring optimal performance.
3.Energy Efficiency:
Efficiently converts electrical energy into heat, providing effective thermal management.
Can be integrated with smart controls and sensors to optimize energy usage and enhance efficiency.
4.Durability:
Designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity, and UV exposure.
Long-lasting performance with minimal maintenance requirements.
5.Customizable:
Available in various sizes, shapes, and configurations to fit different architectural and design needs.
Can be tailored to specific applications and requirements.
Advantages
1)Improved Visibility:
Ensures clear visibility by preventing fogging and icing on glass surfaces.
Enhances safety and comfort in various applications, from vehicles to buildings.
2)Enhanced Comfort:
Provides a warm surface, reducing the feeling of cold radiating from glass windows and doors.
Contributes to a more comfortable indoor environment.
3)Energy Savings:
Reduces the need for additional heating systems, leading to energy savings and lower utility bills.
Can be used in conjunction with other energy-efficient technologies for optimized performance.
4)Aesthetic Appeal:
Maintains a sleek and modern appearance without the need for visible heating elements or bulky hardware.
Suitable for contemporary architectural designs.
Applications
1.Residential:
Used in windows, skylights, glass doors, and bathroom mirrors to prevent condensation and maintain clear visibility.
Enhances comfort and energy efficiency in homes.
2.Commercial:
Employed in storefront windows, glass facades, and atriums to prevent fogging and frost buildup.
Supports modern office designs and improves energy efficiency.
3.Automotive:
Integrated into car windshields, rear windows, and side mirrors to prevent fogging and ice buildup.
Enhances driving safety and visibility, particularly in cold weather conditions.
4.Aerospace:
Used in aircraft windows and cockpit windshields to prevent ice and fog formation.
Ensures clear visibility and safety for pilots and passengers.
5.Marine:
Applied in yacht and boat windows to prevent condensation and maintain clear visibility in marine environments.
Enhances comfort and safety for passengers and crew.
6.Healthcare:
Employed in hospital and clinic windows to prevent condensation and improve patient comfort.
Supports hygiene and clarity in medical environments.
7.Retail:
Used in display cases and storefront windows to prevent condensation and enhance product visibility.
Creates an appealing shopping environment and attracts customers.
8.Public Transportation:
Integrated into train and bus windows to prevent fogging and ice buildup, ensuring clear visibility.
Enhances passenger comfort and safety.
Installation and Usage
Installation:
Requires professional installation to ensure proper alignment, electrical connections, and integration with existing systems.
Available as laminated glass with embedded heating elements or as glass with a conductive coating.
Power Requirements:
Operates on standard electrical voltage, with specific requirements depending on the size and configuration of the heated glass.
Power supply units (PSUs) and control systems are used to regulate the electrical current and optimize performance.
Control Options:
Can be controlled using wall-mounted switches, thermostats, or integrated into smart home and building automation systems.
Some systems offer smartphone app control for added convenience and automation.